Yes! Common Cold Can Cause Hearing Loss. Learn Ways To Reverse It
An infection of the upper respiratory tract, including the nose, throat, nasal passages, and larynx is commonly known as a cold. Common colds can cause nasal or sinus congestion, which can make your nose feel stuffy. Do you know that the cold can sometimes be the cause of an ear infection, which, in addition to earache and fever, can also cause temporary hearing loss? Usually, colds are mild, but they can cause some nasty side effects, such as temporary hearing loss.
When a person is congested, the fluid and mucus can reach the Eustachian tubes in the ear. Eustachian tubes connect the middle ear to the back of the throat, remove fluid, and prevent accumulation in the middle ear. This accumulation of fluid buildup in the middle ear is likely to make it hard for sound waves to be transmitted into your ears and eardrums. This can lead to muffled hearing or temporary hearing referred to as transient conductive hearing loss.
In cases of both a cold and ear infections, your hearing should return to normal in a few days as you start to get better and other associated symptoms fade.
How Cold Affects Your Hearing
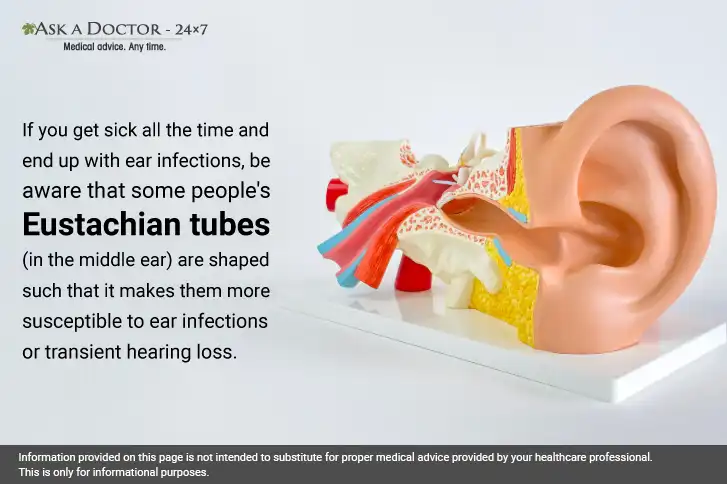
Let us understand how the common cold can affect your hearing:
1. Ear Congestion: One may experience clicking in the ear when affected by a cold. Additionally, conversations and ambient noises may take on a muffled quality. These are indicative of congestion stemming from a buildup of fluid within the middle ear. Such congestion can potentially progress to an ear infection caused by bacteria or viruses, resulting in temporary hearing loss. The fluid frequently remains in the middle ear for several weeks or even months, ultimately resolving independently. However, if the issue persists, it is advisable to contact your physician. Once an ear infection clears, normal auditory function should return.
2. Ear ringing: Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, can begin or increase with a common cold or the flu. Typically, the ringing reduces when cold symptoms go away.
Medical professionals advise individuals with a cold to do the following:
- Get plenty of rest.
- Avoid strenuous activity.
- Stay hydrated.
- Prevent the spread of germs.
- Over-the-counter medications, such as decongestants.
3. Ear pain and other serious sickness: Typically, a cold lasts seven to ten days. Cold often reduces the immune response by killing off bacteria-fighting cells in the nose. However, a cold has the potential to worsen into something more serious, like:
- Coughing up large amounts of mucus
- Ear infection
- Earache
- Inability to keep down fluids or foods
- Facial pain, throbbing headache, or a painful sore throat that interferes with swallowing
- Unusual tiredness
- A high fever lasting more than one day
- Chest or stomach pain
- Swollen lymph nodes
4. Prolonged symptoms: Prolonged fluid accumulation in the ear, lasting several weeks, may exert pressure on the hair cells within the inner ear. This pressure can potentially damage the hair cells, resulting in irreversible, permanent hearing loss.
Ways to Reverse Hearing Loss Due to Cold

Remedies to treat clogged ears due to cold include:
- Warm compress or steam: Consider taking a hot shower or applying a warm compress using a warm wet towel over the nose and forehead. Steam clears out the mucus from inside our bodies. You can also breathe in steam from a bowl or use a humidifier or vaporizer.
- Gargle with salt water: Salt water is a natural solution for many issues involving mucus buildup in the nose or ears. Additionally, it can stop several infections from happening. To gargle, dissolve a half-spoonful of salt in one glass of water. To relieve sore throats, keep water warm. For ear relief, gargle 15–20 times and spit the water out.
- Consider essential oils: Natural essential oils like tea tree oil, peppermint oil, and eucalyptus oil have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties. They can clear the mucus and reduce inflammation. You can use them as ear drops after consulting with your doctor.
- Ginkgo biloba: This herb is well renowned for its capacity to enhance blood flow, which in some circumstances might enhance hearing. It's vital to consult your doctor before taking this herb.
- Decongestants: Decongestants are available over the counter that help alleviate fluid buildup and help with hearing loss.
When to Consult a Doctor
Hearing loss caused by cold is often transient and mild. But if a person encounters any of the following, they should immediately consult a physician:
- Prolonged hearing loss, more than 15 days
- Drainage or pus discharge from the ear
- Severe ear pain
- Dizziness
- Eustachian tube dysfunction
- Ringing or an unending sound in the ear
- Very high fever
- One-sided hearing loss
- An unusual neurologic sign that includes facial paralysis, a weak blink, or sudden loss of hearing
We have learned so far that the common cold can lead to temporary hearing loss. During a cold, the fluid that builds up in your nose, sinuses, and throat blocks your ear and nose tubes, preventing them from draining out. The majority of temporary hearing loss will go away on its own, but you may also need to use a decongestant to help clear your ears and nose. Also, prolonged congestion and untreated ear infections have the potential to cause irreversible hearing loss. Hence, consult your healthcare provider or Otolaryngologist / ENT Specialist Online to prevent permanent damage to your hearing.
If you have any questions about cold-related hearing loss, you can Ask an ENT Specialist at Ask a doctor, 24x7.
Recently Answered Questions Related to Hearing and Ear Health
- Aural Fullness, Tinnitus, Hearing Loss, Dizziness. History Of Cold, Sinus Infection. Causes For Symptoms?
- Do Earache, Cold And Fever Require Medical Attention?
- What Are The Treatment Available For Sensorineural Hearing Loss?
- Child Suffering From Cold And Sneezing. Having Hearing Loss. How To Cure This?
- Suggest Remedy For Cold, Cold Sores And Dizziness
- What Causes Hearing Loss, Tinnitus And Cold?
- Suggest Remedy For Recurring Cold & Cold
- Catch Cold After Eating Cold Products Or Staying Cold. Migraine And Sinusitis? Treatment?
Disclaimer: Information provided on this page is not intended to substitute for proper medical advice provided by your healthcare professional. This is only for informational purposes.
Ask a Specialist
Recent Questions


