All You Need To Know About Core Body Temperature
Our body temperature is one of the most vital indicators of our health. It is why checking temperature is an essential part of our routine health-check – done at all the health care centers, and we too do it at home when not feeling well. Still, you would be surprised to know that many people are actually not aware of what’s a “normal” human body temperature. Yes, you read it right!
Here, in this write-up, our expert details all about core body temperature that you must know. Read on...
Body Temperature: What’s normal?

Most of us have grown up being told that 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit (or 37 degrees Celsius) is the body’s normal temperate. Nevertheless, the fact is there isn’t one exact “normal” body temperature for all, claim studies. Yes, everyone has their own ordinary. For adults, a normal body temperature may vary anywhere between 97 to 99 degrees F. Kids have a slightly higher range than adults and it varies between 97.9 degrees F to 100.4 degrees F.
Moreover, to your surprise your body temperature does not remain the same all the time, it may fluctuate throughout the day.
Understand the Mechanism of Body Temperature

A healthy body always keeps the temperature at a comfortable level. If a person is out in the cold, their skin may feel numb or frozen, however, their core body temperature from within will still remain within normal range.
The hypothalamus (a part of the brain) is responsible for this thermostat. When the body experience severely cold temperatures, the hypothalamus sends a signal to the body to preserve heat by shrinking blood vessels and producing heat that leads to shivering. The reverse happens when the body gets too hot – the hypothalamus would signal the body to produce sweat to cool off.
Many studies show that one’s core body temperature reduces with age. Hypothyroidism also causes a decrease in core body temperature. Extremely cold temperatures and certain medications can cause hypothermia (reduced body temperature). It is an emergency condition and would require a doctor’s attention.
8 Common Conditions that Lead to Fluctuation in Body Temperature

There are a few factors that may affect a person’s body temperature, such as:
1. Age
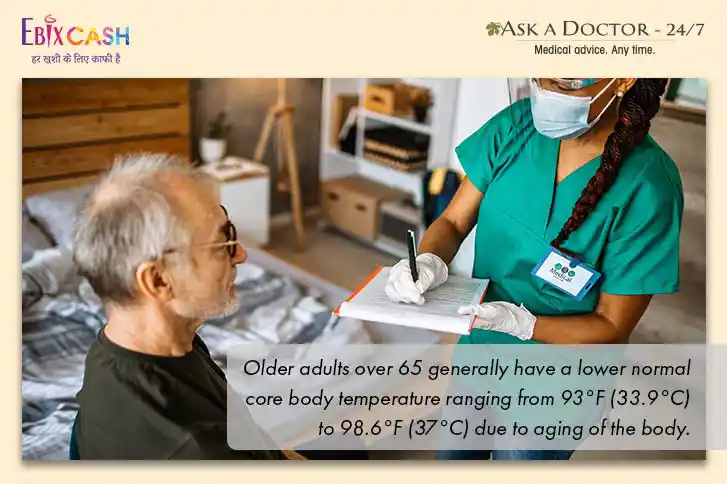
With advancing age, as the body deteriorates, the slowing down and diminution reflects on all bodily functions which include the maintenance of one’s core temperature.
2. Gender

Studies show that the temperature of women’s extremities (hands and feet) lowers noticeably first. As men generally have more muscle mass compared to women, it helps generates more heat naturally. Women having a relatively higher surface area to volume ratio with smaller stature tend to lose body heat fast.
3. Time of the day

There is an internal thermostat in our body that helps gradually increase our core temperature for the day from the time we wake up. Typically body temperature remains lowermost early in the morning and highest late in the afternoon. The body follows the circadian rhythm to adjust its temperature.
4. Low and high levels of movement

Upon movement, our muscles need the energy to expel, and during this process, the body generates high levels of heat which in turn increases the body’s overall core temperature. During strenuous exercise, the heat produced by the body may exceed 1000 W, and to regulate this, the blood vessels carry the heat to the skin. Once the sweat evaporates and heat is lost from the blood vessels, the system gradually cools down.
5. Intake of food and fluids

Our metabolic rate (energy consumed) increases to help with the digestive process and this consumption of energy to process food increases the amount of heat generated in the body. Thus, leading to an overall increase in one’s body temperature.
6. Menstrual cycle in females

During the phase of the monthly menstrual cycle in females, a difference in body temperature can be noticed. It's usually lower in the first part of your cycle, while it rises when a female ovulates.
7. Lesser than normal metabolic rate

One of the main factors that affect our body temperature is our metabolic rate. Like a car engine on idle, the body also spends energy to just keep things going, and this in itself produces heat. A low metabolic rate at other times could be because of higher body mass, good therapeutic treatments, precautionary measures, and overall health.
8. Inflammation and Infection Rates

Wunderlich’s day, tuberculosis, syphilis, chronic gum disease, and other inflammatory situations can increase the body temperature of the patient, and here, the treatment is limited.
Besides the above, our body temperature can also be variable when measured at different parts of the body, such as oral (mouth), rectal (bottom), or armpit readings.
Checking on one’s body temperature when not well is a good practice. In case the temperature is not within the normal range and is either too high or too low, consult an Internal Medicine Specialist, and relate all the symptoms including the fluctuation in body temperature for an accurate prognosis.
Stay aware to stay healthy!
Ask a Specialist
Recent Questions


