Know All About Vitamin D Deficiency
Out of all the micronutrients we consume, vitamins play a vital role in our base metabolism. When we have low levels of vitamin B12 or B9 (folate) it leads to deficiency of vitamins. This condition usually occurs when our body doesn’t produce enough healthy red blood cells or if one has a disorder that makes it difficult for the body to absorb nutrients.
Here in this write-up, we will help you know about type of vitamins with detailed explanation on Vitamin D deficiency, its prognosis, its associated complications, treatment and more. Read on…
Types of Vitamins

Vitamins are of 2 types, water soluble vitamins like B and C, and fat soluble vitamins like A, D, E and K. All vitamins are essential for normal metabolism and must be obtained through diet. Amongst the above, vitamin D is even synthesized in our body otherwise, apart from being consumed via diet.
All About Vitamin D

Vitamin D belongs to a group of fat-soluble secosteroids which is involved in the absorption of calcium, phosphate, and magnesium from the intestines along with many other biologically important compounds. Only a few food sources exist for vitamin D. A majority of it is synthesized from cholesterol in the skin through chemical reactions which needs UVB radiation from sunlight.
Vitamin D plays an important role in calcium and phosphorous homeostasis and metabolism. Calcium is essential for maintaining bone mineral density in the bones. When the bone mineral density reduces, softening of the bones occurs leading to deformities like rickets in case of children and bone or joints pain in adults known as osteomalacia.
Complications Due to Vitamin D Deficiency
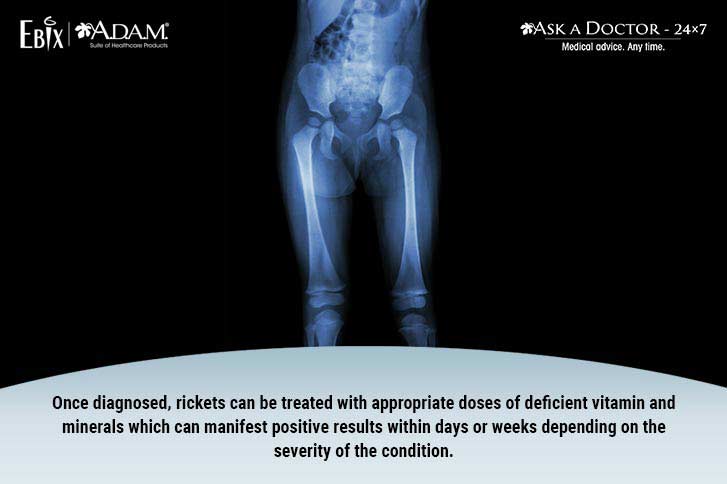
Rickets in children occurs when they are deficient either due to consumption of a Vitamin D deficient diet or less exposure to sunlight. This initiation of pathology is more commonly seen in infancy and progressing into childhood. This is characterized by poor growth, soft, weak, deformed or long bones which tend to bow over time. Overt bone disease can even be seen in newborns when mothers are vitamin D deficient.

Osteomalacia is the counterpart and seen in adults due to low vitamin D levels. This is characterized by the softening of bones leading to bending of long bones, bending of the spine, muscle weakness, increased risk of bone fractures etc. In osteomalacia, due to low vitamin D levels, less amount of calcium is absorbed from the intestines and hence, to compensate, bone calcium is lost into the blood leading to weakness in the bones. These features are overt and appear when the levels are below 10ng/ml.
Range and Grades of Vitamin D Deficiency Simplified

< 10ng/ml - Severe deficiency
10 - 20ng/ml - Moderate deficiency
20-30ng/ml - Mild deficiency
30-80ng/ml - Optimum levels
>80ng/ml - Toxicity possible
As stated above, symptoms and signs of deficiency are seen mostly when the levels drop below 10ng/ml. Although, any value more than 10ng/ml and less than 30ng/ml is considered a deficient state. They may not have symptoms and yet, these are the ones that represent the submerged portion of iceberg whose tip represents the people presenting obvious and apparent deficiency.
Prognosis and Treatment of Vitamin D Deficiency

Mild and moderate deficiency statuses are ones which can progress into a severe deficient state, if not intervened. Vitamin D levels are also connected to insulin resistance and lipid metabolism. Lower levels are known to cause diabetes in pre-diabetics and even in people with risk factors. Lipid metabolism is affected by lower levels of vitamin D. The effect can be such that it can cause dyslipidemia, leading to many other morbidities.
Hence, supplementing with vitamin D even in mild to moderate deficient states is essential. This can avoid the incidence of diabetes and many other metabolic disorders.
Supplementing people with severe deficiency is the treatment when one presents with symptoms. However, it is the submerged portion of the iceberg we have to be careful of in people who have no symptoms and are otherwise normal. Hence, it is always advisable to all irrespective of age and race to get their vitamin D levels checked. When less than 30ng/ml, supplementing will surely prevent major problems before they even start, hence, primary prevention.
Care is to be taken not to supplement people with normal levels of vitamin D as toxicity of vitamin D is also a major concern. Inadvertent use by people on their own has increased the prevalence of toxicity.
To conclude, without being skeptical, vitamin D estimation can be considered a part of routine health check up. This is to prevent noticeable deficiency as we are not sufficiently warned always.
To know more about Vitamins, their role and about their deficiency talk to a Specialist now.
Recent Questions


