7 Things To Know About Neuroendocrine Tumors
Do you know that a rare cancer known as Neuroendocrine Tumor (NET) can develop in the neuroendocrine system? Our neuroendocrine system consists of nerve and gland cells that release hormones into the bloodstream. Like nerve cells, these abnormal cells receive messages; like endocrine cells, they can release hormones.
NET is a complex and misunderstood disease affecting thousands worldwide, yet it remains under-recognized. Let us understand the seven key facts about this condition to better recognize it, early diagnose it, treat it, and improve the outcome of this elusive disease.
Facts About Neuroendocrine Tumors
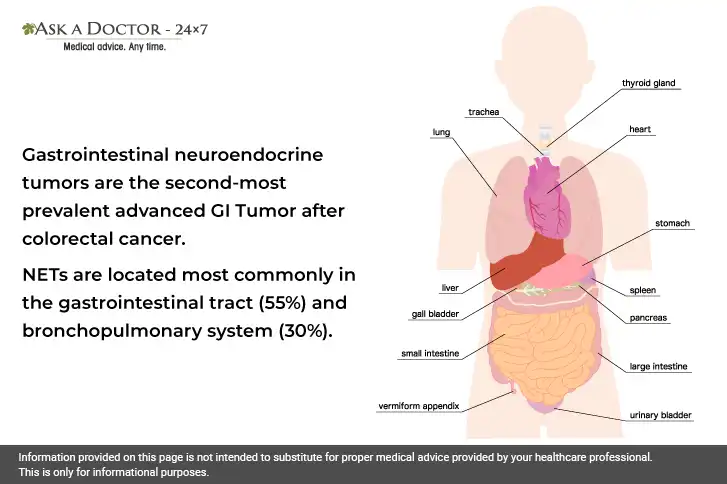
Let us understand neuroendocrine tumors:
1) Neuroendocrine tumors can develop anywhere
Neuroendocrine tumors can develop anywhere where endocrine cells are present. Endocrine cells control several bodily processes, including metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Although found all over the body, they are most frequently formed in the digestive system (stomach, small intestine, large bowel, and appendix), pancreas, and lungs.
2) Rate of growth
Usually, NET tumors develop slowly but can grow aggressively and spread to other body areas. The location of the tumor site can be added to the NET terminology, such as lung NET and pancreatic NET (PNET).
Common symptoms of NET
Some types of NETs do not cause symptoms, while others cause general gastrointestinal and respiratory symptoms that mimic more common diseases. Neuroendocrine tumor symptoms typically fall into one of two categories:
- Hormonal neuroendocrine symptoms: It results in severe diarrhea, abdominal pain or cramping, severe stomach ulcers, facial flushing or uncontrolled blood sugar, and asthma-like wheezing that doesn't improve with treatment. The type of hormone production depends on where the tumor originates in the body.
- Mechanical neuroendocrine symptoms: A small intestinal blockage or pain in a specific location is an example of mechanical neuroendocrine symptoms. The tumor's physical pressure on another structure causes these symptoms.
Causes of NET
The exact cause of NETs is unknown but some NETs have been observed to occur more in people with inherited genetic conditions. This includes:
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia
- Neurofibromatosis
- Von Hippel-Lindau disease
Other possible factors that may increase the risk of developing NETs are:
- Gender and age: Men are slightly more likely than women to have NETs.
- Having male Black African ancestry
- Pre-existing gastrointestinal disorders, like peptic ulcer
How NET is Diagnosed?
NET diagnosis is often difficult. NET tumors can develop anywhere in the body and are frequently very small, so diagnosing them can be challenging. Some NET symptoms are frequently non-specific, so these tumors are sometimes mistakenly diagnosed as common ailments. Diagnosis includes blood tests, biochemical markers testing, imaging scans, and biopsies.
Treatment of Neuroendocrine Tumors
Doctors can treat NETs with surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and drugs. However, the selection of treatment depends on:
- The type of tumor and its number
- It's malignant or benign
- Whether other areas of your body have been affected as well due to spread
For NET treatment, currently, surgery is the only effective curative therapy option, particularly if the tumor is in one location. If the NET has not spread, the tumor can be completely eliminated through surgery, leaving behind healthy tissue. In this case, there is no need for additional therapy because the surgery may be able to cure the malignancy. Surgery may also be necessary to reduce the size of the tumor if it is too big to remove entirely to shield the surrounding organs.
Depending on the growth and spread of NET, chemotherapy and radiotherapy may also be recommended along with surgery and other medical therapies.
7) Complications of Neuroendocrine Tumor
When a neuroendocrine tumor in your lungs or gastrointestinal tract releases an excessive amount of hormones, it might cause carcinoid syndrome. Wheezing, diarrhea, and flushing—a rapid warmth and redness of the head and neck—are just a few of the unpleasant symptoms it can produce.
If left untreated, carcinoid syndrome may cause more difficulties, and it may pose a threat to life rarely. Carcinoid syndrome is lessened when NETs are treated.
Hence, malignant cancer cells that develop in the neuroendocrine system are known as neuroendocrine tumors. How a NET affects you, depends on the kind of tumor you have, whether it's cancerous, and how much it has spread. But with the right treatment, doctors might be able to shrink the tumors or get rid of them completely. Take charge of your health and feel more confident by discussing your NET diagnosis and treatment plan with your healthcare professional.
If you have any questions about neuroendocrine tumors, you can Consult an Oncologist online at Ask a Doctor - 24x7.
Recently Answered Questions Related to Neuroendocrine Tumors
- Is There Any Type Of Neuroendocrine Tumor That Can Cause Ileitis?
- Suggest Prognosis For Patient With Neuroendocrine Tumor
- Can Lithium Dotatate Be Taken For APUDomas?
- What Causes Hot Flashes, Cold Sweats And Vertigo In An Elderly Woman?
- What Causes Loss Of Weight After Treating Neuroendocrine Tumor?
- Carcinoid Syndrome, Biopsy Showed Castlemans, Tumor In Liver, Rituxan Chemotherapy, Flushing, Diarrhea, Nausea, Vomiting, Fever
Disclaimer: Information provided on this page is not intended to substitute for proper medical advice provided by your healthcare professional. This is only for informational purposes.
Ask a Specialist
Recent Questions


